If you just want to see how to create a proxy server in Next.js, click here!
The Problem
Sometimes you need to fetch some data. Often, when you're just learning programming, you'll be fetching that data from some place you don't own, data that has a different 'origin' than your local computer. However, when you try this, more often than not, you'll run into this issue:
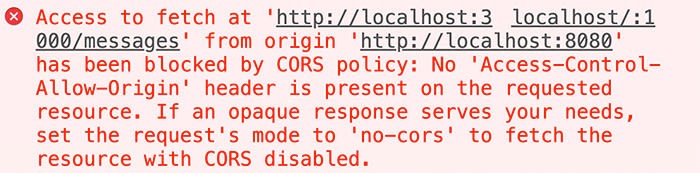
This is a security feature that prevents you from fetching data from a different domain. Ultimately, this is a necessary feature, but it can be a pain when you're trying to learn how to fetch data from an API.
What is CORS?
CORS, or Cross-Origin Resource Sharing, is a mechanism that lets servers describe which origins are permitted to read their information from a web browser. Basically, it allows origins other than its own to access its data, if explicitly allowed. JavaScript's fetch() follows what's called a same-origin policy, which is a security feature that prevents one origin from making requests to a different origin. This is essentially what causes the above error. This is a good thing because it prevents malicious websites from making requests to your bank, your email, or your social media accounts while using cookies that may contain sensitive information. However, it can be a bit annoying when you're trying to learn how to fetch data from an external API. Luckily, there is a way we can get the data we need while still following the same-origin policy.
Proxy Servers
Enter the proxy server. In a nutshell, a proxy server acts as a middleman between you, the client, and the server you're requesting data from. You simply send a request to this proxy server, saying that you want to access some data from a server of a different origin, and it will make the request on behalf of you. If you want to know why a proxy works and why it doesn't technically "bypass" CORS, there's a great thread on the /r/webdev that contains some simply put answers.
Creating a proxy server with Next.js
Now on to the code! Luckily, with Next.js, it's really easy to create a server within your app. For simplicity, in this example, I'll be using the base app code generated from create-next-app. We'll also be using Next.js's App router as opposed to the Page router, though the solution for both doesn't differ much.
npx create-next-app@latest
Once you have your app set up and ready to go, navigate to your main project directory. Inside, you should have an app directory with your main page and layout file. This is where our proxy server code will live. Now I should mention that in Next.js, components are server components by default, which means you could make a proxy request directly from any server component, and it will avoid CORS errors. However, I'd prefer to keep my server requests in a separate file and make use of Route handlers, so that I could call this code from any of my client components and save the returned data using useState.
Setup your Route Handler
To create a route handler, we need to first create a new folder in your app directory. It can be named anything, but I've named mine api. Inside the new api folder, create a file named route.js|ts. This is your route handler, and this is where we'll be making our proxy request. Your app folder should now look something like this:
└── app├── api└── route.js├── page.jsx├── layout.jsx
Inside your route file, you'll create an async function, with the name being the type of HTTP request you'd like to make. For our example, I'll be making a GET request, so the function definition will look like this:
ts// HTTP method is a GET requestexport async function GET(request: Request) {...}
All that's left from here is to build out your request in the function body. In my example, I'll be fetching some raw HTML from a recipe URL with the intent to process its metadata. If I attempted this on the client side, I would be faced with a CORS error. From here, I'll use the fetch API to make a request to the recipe URL and then return the response. Here's what my code looks like:
tsexport async function GET(request: Request) {// Fetch the data from the recipe urlconst res = await fetch('https://www.foxandbriar.com/oven-baked-greek-chicken-thighs/', {headers: {'Content-Type': 'text/html',},})// Response will be a string of HTML, as opposed to the usual JSONconst data = await res.text()// Return the response, along with the status codereturn new Response(data, { status: res.status })}
And done! Now all that's left is to call the route handler from a client component. To do this, you can simply fetch the route inside your component. Here's what that looks like:
tsx"use client";import { useEffect, useState } from "react";export default function Home() {const [myHTML, setMyHTML] = useState("");useEffect(() => {fetch("http://localhost:3000/api/proxy").then((response) => response.text()).then((data) => {console.log(data);setMyHTML(data);});}, []);return (<main>...</main>);}
You can also see the result of your fetch by visiting the route directly in your browser. You should see the data of your request.
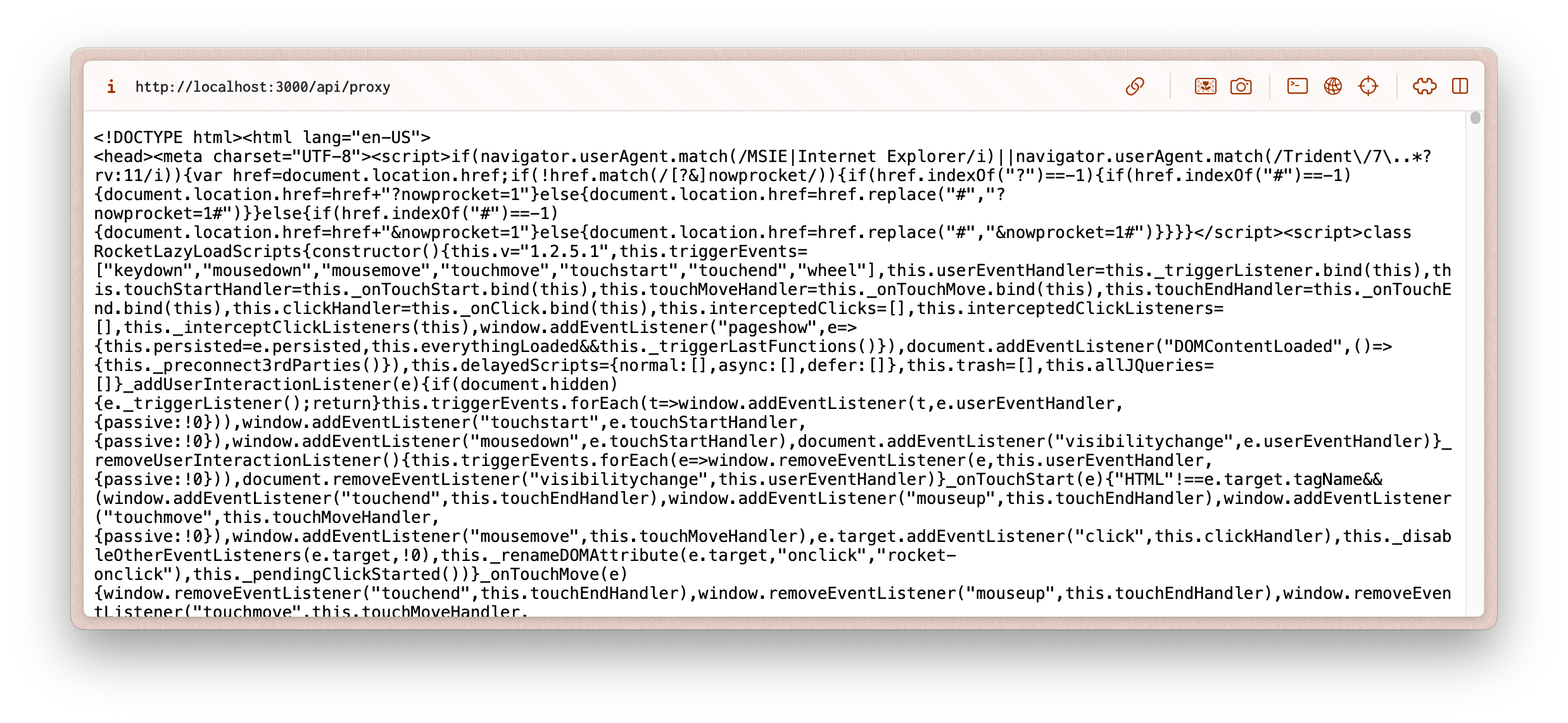
And that's it! You've successfully created a proxy server with Next.js. Now you can fetch data from different origins without having to worry about CORS errors. Hopefully this helped you out, and if you have any questions or concerns, feel free to shoot me an email. Happy coding!